Introduction
sRNAPrimerDB is composed of multiple primer designing programs, combined with calculated primers. It allows users to search and design primers for small ncRNAs, such as miRNAs and piRNAs. The database is composed of eight divisions including a section for designing, a bank of pre-designed primers and probes, a searching tool as well as links towards scientific literature and resources. Primers for small ncRNAs that have been experimentally validated are encouraged to submit an online application form by visiting our web site at sRNAPrimerDB.
Downloads:
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
We have been developing algorithms HidPET (Hierarchical and Dynamics Analysis of TF Cooperation with ChIA-PET and ChIP-Seq Data) to facilitate the analysis of Chromatin Interaction Analysis with Paired-End Tag (ChIA-PET) and Hi-C, ChIP-Seq and DNA methylation data, and use integrative modeling approaches to study genomic transcriptional, 3D genome organization and epigenetic gene regulatory mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and progression. We are developing new methods to utilize the abundant public ChIP-seq data to infer functional enhancers that regulate the expression, and understand the targets and specificity of epigenetic factors in cancers.
Donwloads
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
Nuclear receptors play important roles in various biological processes and are a group of proteins with the ability to directly bind to DNA and to regulate the expression of genes. Although decades of work have been done in this field, their binding mechanism has still been not fully understood. With the development of next generation sequence technology, vast amount of nuclear receptors binding sites have been identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by massively parallel sequencing (ChIP-Seq). There is a great need to construct a database incorporated different nuclear receptors at various conditions to improve our understanding of binding mechanism. To fulfill this demand, we have developed a software NR-HMM for predicting Nuclear Receptor binding sites based on a Hidden Markov Model framework and applied it on 38 Chip-seq datasets for mouse. NR-HMM can facilitate the analysis the Cooperation and crosstalk of Transcription Factors and use integrative modeling approaches to study genomic transcriptional and epigenetic gene regulatory mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and progression.
Downloads
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
CRISPRamplicon, an analysis tool that unites identification, quantification and visualization of genuine genome editing events from High-throughput sequencing data, for example, CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) amplicon sequencing data, Target capture sequencing data, Whole exome sequencing data, and Whole genome sequencing data, etc.
Downloads
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
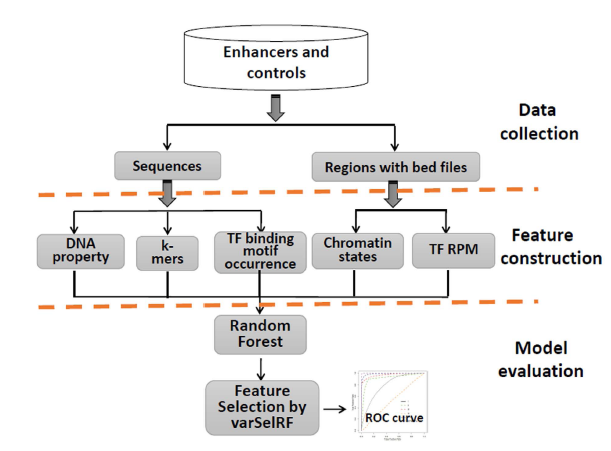
In silico method to identification of enhancers on the basis of a combination of transcription factor binding motif occurrences. Enhancers can interact with gene promoters to form chromatin looping structures for important functions in various biological processes, such as gene transcription regulation and cell differentiation. However, enhancers are difficult to identify, since they usually do not have fixed position or consensus sequence features, and the biological experiments for enhancer identification are costly in labor and expense. In this wok, several models have been built using various sequence-based feature sets and their combinations for enhancer prediction. The selected features from a recursive feature elimination method show that the model with the combination of 141 transcription factor binding motif occurrences from 1422 transcription factor position weight matrixes can achieve reasonably high prediction accuracy, which is superior to other reported methods. The models showed quite good prediction accuracy on different enhancer data sets from different cell lines/tissues. In addition, the prediction accuracy could be further improved by integration of chromatin states. Our method can be complementary to wet-lab experiment methods and provide an additional method for enhancer identification.
Downloads:
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
TAD boundary and strength prediction by integrating sequence and epigenetic profile information. Topologically associated domains (TADs) are one of the important higher order chromatin structures with various sizes in the eukaryotic genomes. TAD boundaries, as the f lanking regions between adjacent domains, can restrict the interactions of regulatory elements, including enhancers and promoters, and are generally dynamic and variable in different cells. However, the influence of sequence and epigenetic profile-based features in the identification of TAD boundaries is largely unknown. In this work, we proposed a method called pTADS (prediction of TAD boundary and strength), to predict TAD boundaries and boundary strength across multiple cell lines with DNA sequence and epigenetic profile information. The performance was assessed in seven cell lines and three TAD calling methods. The results demonstrate that the TAD boundary can be well predicted by the selected shared features across multiple cell lines. Especially, the model can be transferable to predict the TAD boundary from one cell line to other cell lines. The boundary strength can be characterized by boundary score with good performance. The predicted TAD boundary and TAD boundary strength are further confirmed by three Hi-C contact matrix-based methods across multiple cell lines. The codes and datasets are freely available at pTADS.
Downloads:
If you use this program in your research, please cite:
Introduction
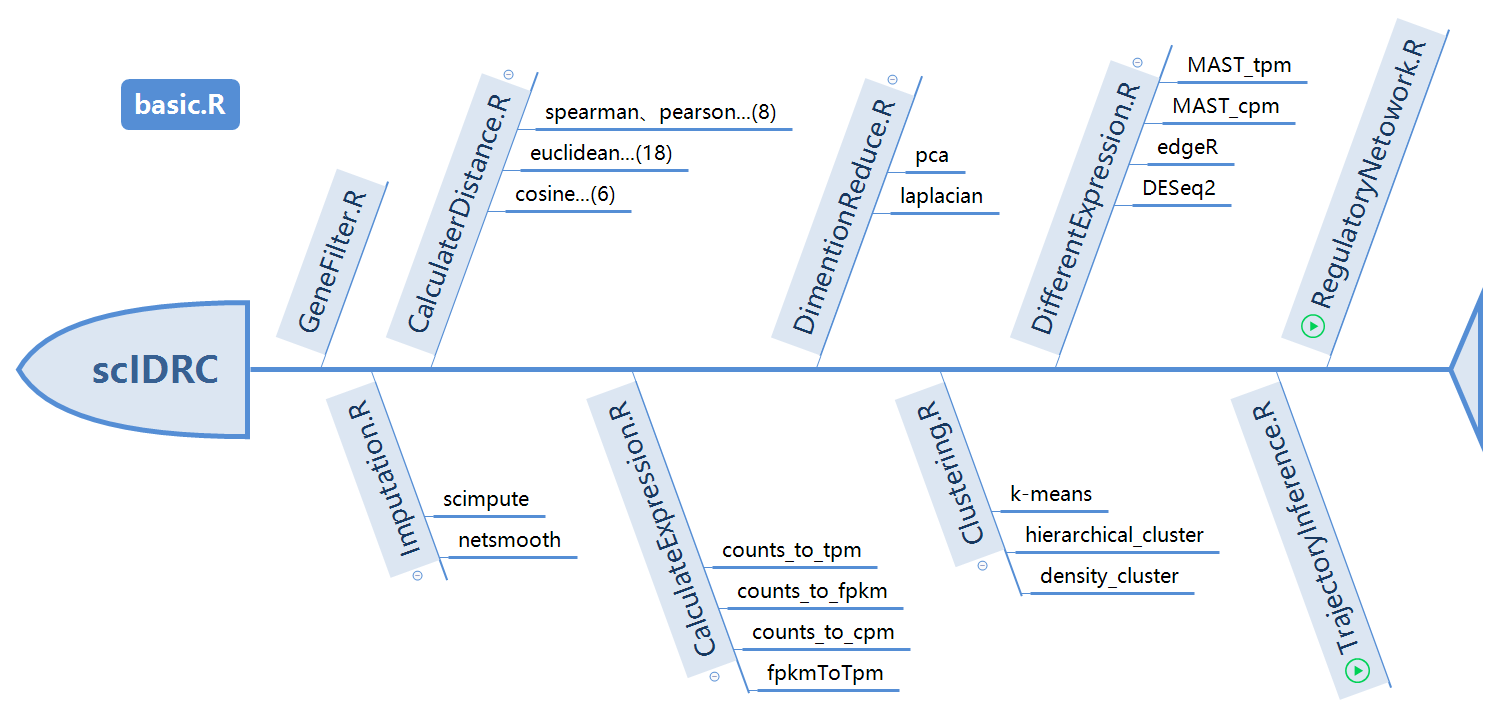
ScICDT (single cell RNA-Seq pipeline for imputation, clustering, distance calculation and dimensionality reduction, pseudo-time and trajectory inference) offers a systematic manner to analyze single cell RNA-Seq data. The package includes methods for sequence data preprocessing, data imputation, expression matrix preparation, distance calculation, dimensionality reduction, clustering, differential expression, pseudo-time and trajectory inference, results evaluation.
Downloads:
Coming Soon!